TECHNIQUES
From bio-revitalization to bio-restructuring
What does it mean to carry out a bio-revitalizing treatment?
The concept of bio-revitalization includes the use of substances which are mainly capable of improving cellular homeostasis. Amino acids, vitamins and high molecular weight linear hyaluronic acid are at the basis of these techniques.
What does it mean to carry out a bio-restructuring treatment?
Bio-restructuring is based on the use of cellular mediators, whose function is to stimulate the cell to produce better and in greater quantities.
What are PDRNs?
Polydeoxyribonucleotides or PDRNs are the molecules that make up our DNA, our genetic code, which is why they are very precious molecules for the body and cells.
Their main feature, in addition to transmitting genetic information, is that of being able to activate many cell membrane receptors, and trigger biological processes that are fundamental for the life of the cells themselves.
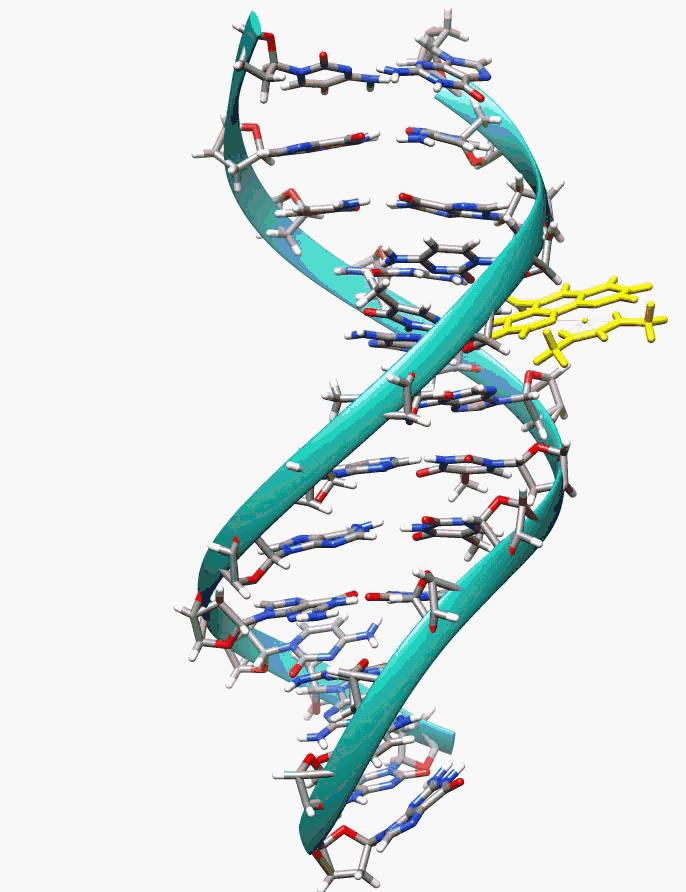
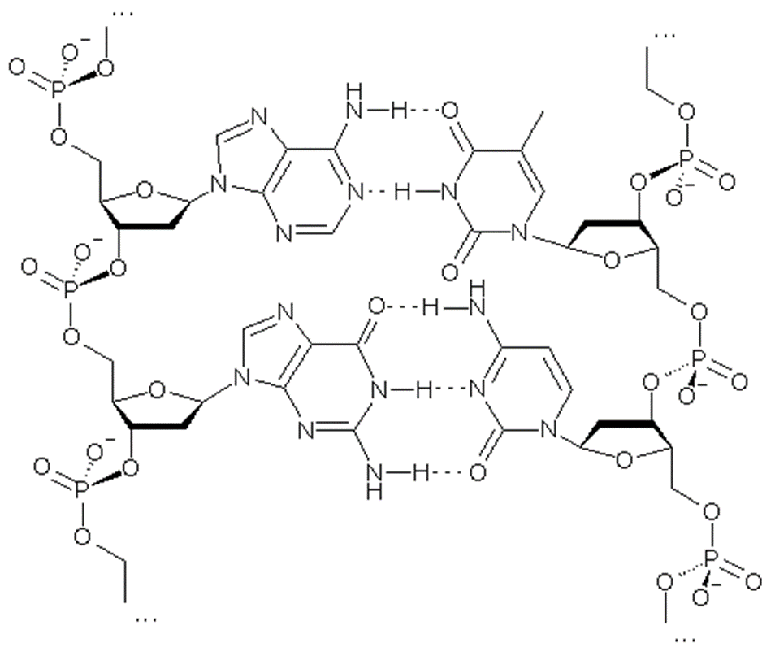
Chemical structure
Polynucleotides are biopolymers of monomer nucleotide, which consists of nitrogenous bases, furanose sugar (deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA), and a phosphate group thanks to a condensation reaction.
It is possible to have 4 type of nitrogenous basis:
Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine
The chemical structure of PDRNs is highly hydrophilic
Features in a nutshell
Products extracted from wild salmon sperm
Highly purified (they undergo a strong purification process)
Low concentration of heavy metals (< 0,02 ppm)
Variable polynucleotides concentration
Variable molecular weight: high, medium, low

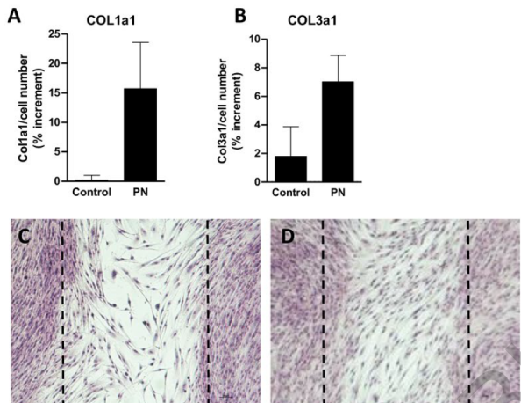
What PDRNs do?
Stimulate the in vitro production of Collagen 1A1 and Collagen 3A1;
Improve the cell number in human fibroblasts culture;
Enhance wound healing in vitro and in vivo;
Stimulate the proliferation of a wide range of cell types (adipocytes, osteoblasts, endothelial cells, glial cells, keratinocytes).
Pharmacokinetics
Hydration (swelling effect) 1-2 h
Metabolic activation (link to the receptors) 48 h
Enzymatic degradation 7-10 days
Complete elimination 15 days
How PDRNs work?
The chemical structure of PDRNs is able to activate specific cellular receptors based on the type of implant that is performed.
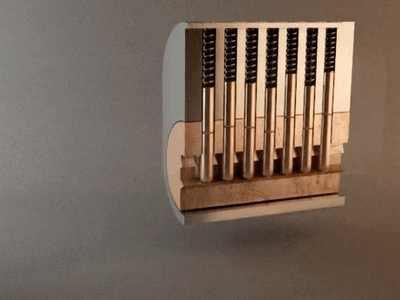
Activation is comparable to triggering the mechanism of a lock, where the key is the PDRN and the lock itself is the cell’s receptors.
Different locks represent different receptors, which will open different doors, triggering different mechanisms within the cell.
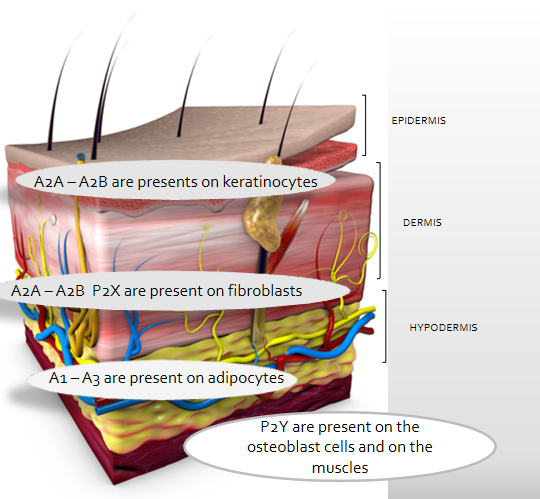
The receptors
Purinergic receptors are present on different types of tissues.
Receptors A2A and A2B have been found in epidermis and dermis; receptors A1 and A3, instead, in the hypodermis.
The extraordinary thing is that these receptors trigger different metabolic pathways according to the depth of their location.
Molecular weight of PDRNs
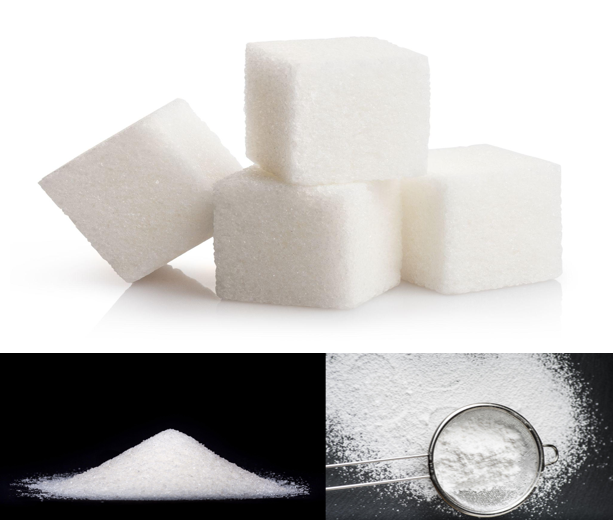
The structure of polydeoxyribonucleotides can be modified according to the size of the molecular aggregates.
As the sugar, it is possible to find it in different forms, granulated in cubes or in extra fine powder. The substance is always the same, only the size of the molecular aggregate changes.
For PDRNs it is the same thing, we can have large aggregates (high molecular weight mixtures), medium aggregates (medium molecular weight) and very small aggregates (low molecular weight).
The structure and the molecular weight are fundamental for the diffusion capacity and for the stimulation’s speed of cellular receptors.

Polynucleotides effects
Moisturizing effect
The strong moisturizing ability is mainly due to the water retention capabilities of the hydrophilic groups of the phosphorylated sugars of the single nucleotides.
An “electrostatic sponge” able to guarantee cellular well-being by conferring deep hydration to tissues.
Effect on fibroblast cells
The activity of P1 receptors is mediated by G proteins that can activate or inhibit Adenylate Cyclase (AC), thus leading to an intracellular cascade of reactions with the final inhibition or stimulation of genes transcription.
P2 receptors stimulation, by ATP and nucleotides, cause an increase of the cellular replication.
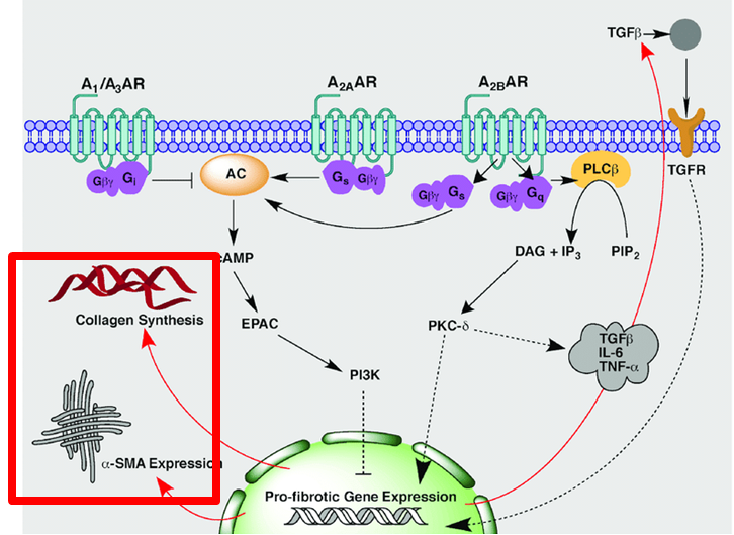
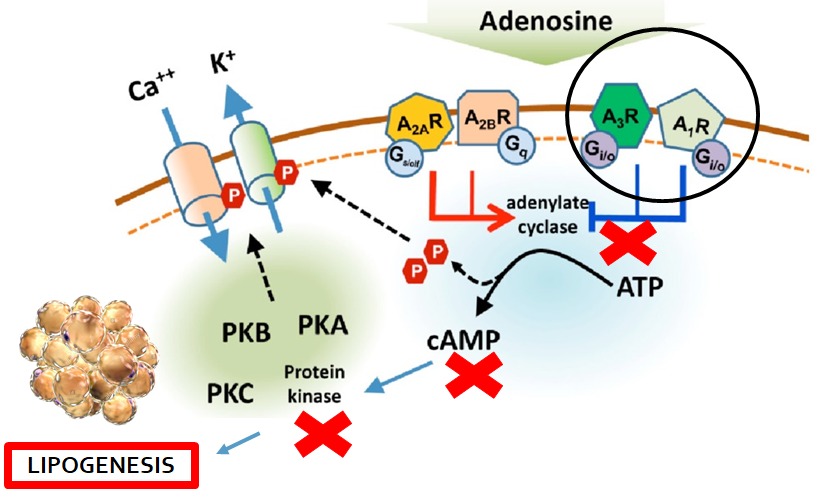
Effect on lipogenesis
When A1 and A3 receptors on the adipocyte binds Adenosine, Adenylate Cyclase is inhibited, thus cAMP is not produced, protein kinases cannot explicate their action and lipase is not able to degrade fatty acids. As a consequence, lipogenesis is indirectly promoted.
The effects of aging in the periocular area
Loss of dermal structure
Superficialization of the capillaries
Reduced blood flow and fluid stasis
Edema, and thinning of the skin

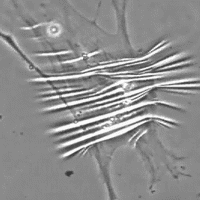
The Gym effect
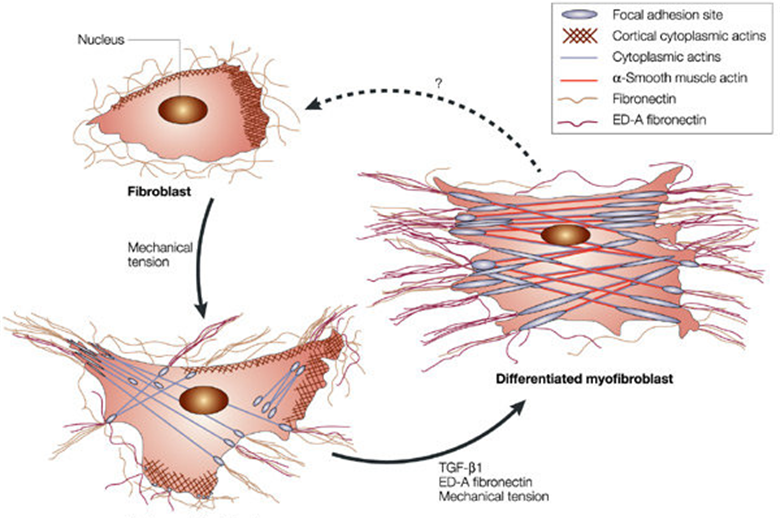
The myofibroblasts are fibroblasts specialized in contraction and they have a peculiar role in establishing tissutal tension.
The Gym effect
The maturation of fibroblasts in myofibroblasts and the production of collagen determines a strong specific lifting and restructuring effect.
The final result is the “LIQUID LIFTING”